Introduction: The Evolution of Design Thinking
Design thinking has long been a cornerstone in innovation, combining creativity with strategic problem-solving. Traditionally, this process relies on human intuition, empathy, and experience. However, with the rise of AI, design thinking is undergoing a transformation, blending human-centric approaches with data-driven insights. This fusion is reshaping how we conceptualize, design, and deliver solutions.
Understanding Traditional Design Thinking
Traditional design thinking follows a well-established framework:
- Empathize: Understanding the user’s needs and pain points.
- Define: Articulating the problem to be solved.
- Ideate: Brainstorming creative solutions.
- Prototype: Building preliminary models or prototypes.
- Test: Evaluating solutions through user feedback.
This iterative process is centered on human observation and insight, often requiring multiple cycles of refinement.
Limitations of Traditional Design Thinking
While effective, traditional design thinking is not without its challenges:
- Time-Intensive: Gathering insights and iterating prototypes can be slow.
- Subjectivity: Decisions are often based on subjective interpretations of user needs.
- Scalability: Scaling these insights for diverse user segments is complex.
These limitations pave the way for integrating AI, enhancing the speed, precision, and scalability of the design process.
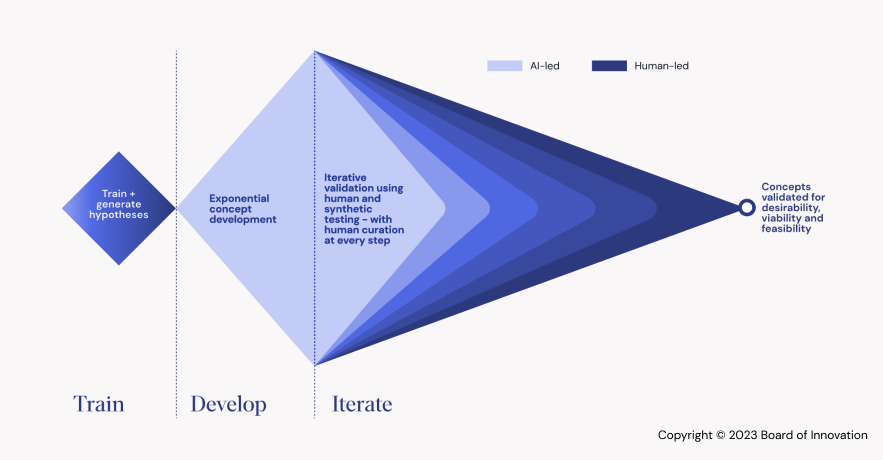
The AI-Enhanced Design Process: A Paradigm Shift
AI introduces data-driven decision-making, pattern recognition, and automation into the design thinking framework. Here’s how AI is transforming each stage:
- Empathize with Data Intelligence: In the traditional process, empathy relies heavily on qualitative research like interviews and observations. With AI, vast datasets can be analyzed to uncover patterns and preferences, offering more objective and comprehensive user insights. AI-driven sentiment analysis tools can quickly analyze user feedback from social media, reviews, and surveys, providing designers with actionable insights.
- Redefining the Problem with Predictive Analytics: AI enhances the problem definition phase by identifying root causes and predicting future user behaviors. Predictive analytics can forecast trends, helping teams redefine problems more accurately and align solutions with evolving user needs.
- AI-Augmented Ideation: During ideation, AI can generate multiple design concepts based on user data, historical designs, and context. Generative design tools use algorithms to suggest design alternatives, allowing designers to explore a broader range of ideas faster. AI also helps in identifying the most viable solutions by simulating user reactions to different concepts.
- Prototyping with Precision: AI accelerates prototyping by optimizing designs and automating repetitive tasks. For instance, AI-powered design tools like Adobe Sensei or Sketch’s smart features streamline the creation of user interfaces by predicting user actions or suggesting design improvements. AI can also simulate interactions and user flows, reducing the number of physical prototypes needed.
- Testing with Real-Time Analytics: AI significantly enhances the testing phase. Instead of relying solely on qualitative feedback, AI-driven tools can track real-time user interactions and behavior metrics across digital platforms. A/B testing, heatmaps, and eye-tracking technologies driven by AI provide granular insights into user experience, leading to more informed design adjustments.
Key Differences Between Traditional and AI-Enhanced Design Processes
| Aspect | Traditional Design Process | AI-Enhanced Design Process |
|---|---|---|
| User Insights | Primarily qualitative, based on interviews and observations | Data-driven, using large-scale analytics and sentiment data |
| Problem Definition | Based on human intuition and experience | Informed by predictive analytics and trend analysis |
| Idea Generation | Manual brainstorming and creative workshops | Algorithmic assistance via generative design tools |
| Prototyping | Hand-crafted and iterative, requiring multiple cycles | Automated, optimized, and guided by AI-driven suggestions |
| Testing and Feedback | User testing with qualitative feedback | Real-time analytics and AI-driven behavioral insights |
Challenges in AI-Driven Design Thinking
While AI enhances the design process, it also presents unique challenges:
- Ethical Design: Relying on AI could result in biased outcomes if data sets are not inclusive or representative.
- Over-Automation: Over-reliance on AI may reduce the human-centric aspect of design thinking, leading to solutions that lack empathy.
- Creativity vs. Algorithmic Constraints: While AI can augment creativity, it can also confine designers within algorithmic boundaries, potentially limiting truly out-of-the-box thinking.
Future of Design Thinking: A Collaborative Approach
The future lies in the synergy between human intuition and AI’s computational power. AI should not replace designers but rather empower them to make more informed decisions, explore diverse ideas, and deliver innovative solutions faster. As AI tools become more sophisticated, the role of the designer evolves from a creator to a curator of intelligent systems.
Conclusion: Embracing the Best of Both Worlds
The integration of AI into design thinking represents an evolution rather than a replacement. By combining the empathy-driven approach of traditional design with the efficiency and precision of AI, designers can unlock new possibilities. The key is to maintain a balance, ensuring that human-centric values remain at the core of innovation while leveraging AI to enhance the process.
This shift is not just about adopting new tools but rethinking how we approach problem-solving in a world where technology and creativity increasingly intersect.



