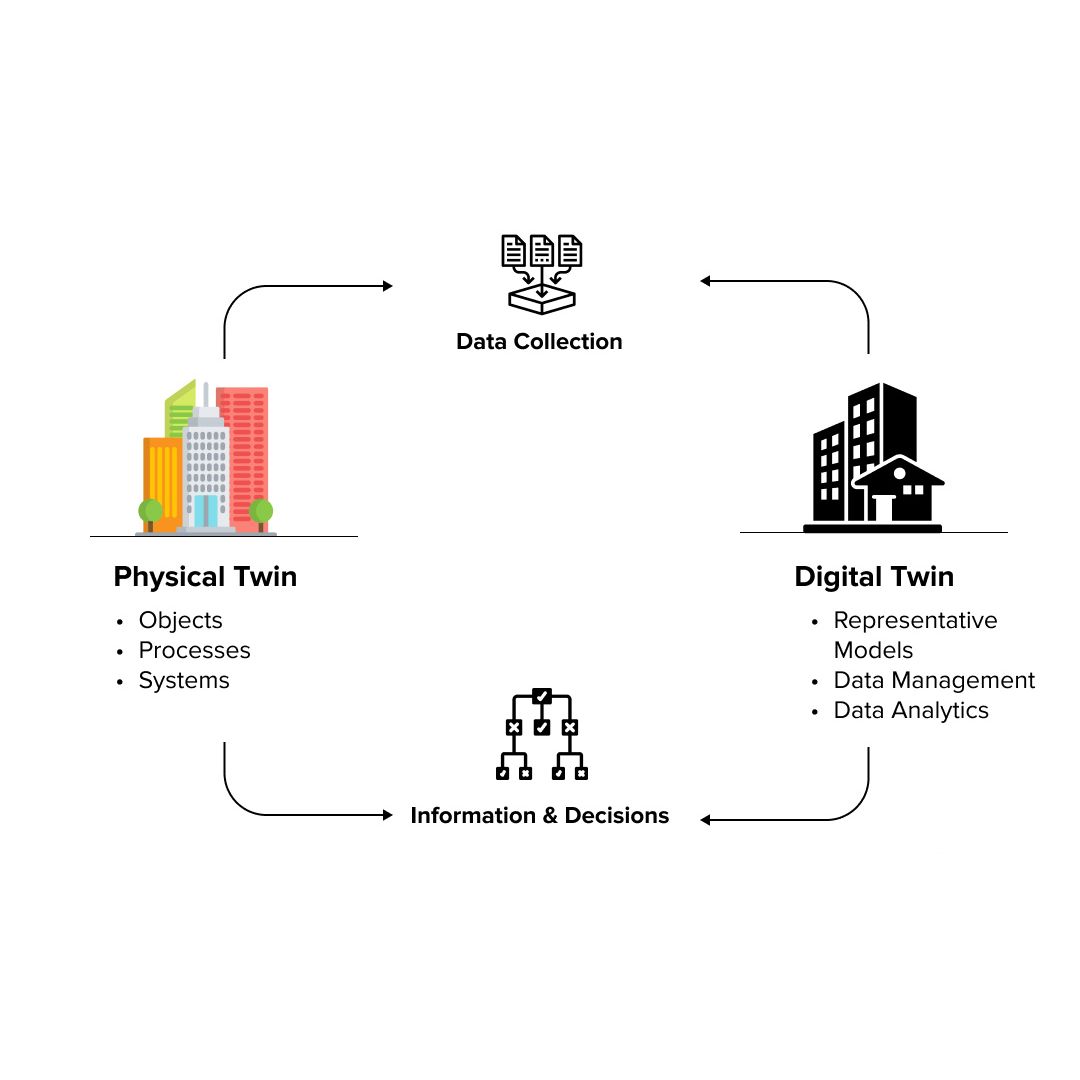
Digital twin technology has been transforming industries from manufacturing to healthcare, and now it’s making its way into retail. With advancements in IoT, AI, and data analytics, retailers can use digital twins to create virtual replicas of their stores, inventory, and even customers. This powerful tool brings real-time data and predictive insights to optimize everything from customer experience to supply chain management. Let’s explore ten use cases and benefits of digital twins in retail, showcasing why they are becoming essential for modern retail strategies.
1. Enhancing Store Layout and Design
Use Case: Digital twins allow retailers to simulate and optimize store layouts before making physical changes. By creating a virtual model of the store, retailers can test various layouts, signage, and product placements to see how they affect customer flow and shopping behavior.
Benefit: Retailers can enhance store layout efficiency and create an enjoyable shopping environment, leading to higher customer satisfaction and increased sales.
2. Inventory Management and Forecasting
Use Case: Digital twins provide real-time insights into inventory levels across multiple stores and warehouses. By integrating with IoT sensors and POS data, digital twins can track product movement and predict future inventory needs.
Benefit: Improved inventory accuracy reduces stockouts and overstock situations, ensuring that customers find what they need while minimizing waste and holding costs.
3. Optimizing Supply Chain and Logistics
Use Case: By creating a digital twin of the entire supply chain, retailers can monitor shipments, forecast demand, and quickly identify potential bottlenecks. They can simulate the impact of supply chain disruptions, such as delays or demand surges, to optimize logistics operations.
Benefit: Increased supply chain resilience and efficiency, leading to reduced delivery times and costs. Retailers can also respond swiftly to disruptions, maintaining a consistent customer experience.
4. Personalized In-Store Experiences
Use Case: Digital twins can model customer behavior and preferences based on data collected from previous shopping experiences. This enables retailers to tailor in-store promotions, product recommendations, and store layouts to individual customer profiles.
Benefit: Delivering a highly personalized experience enhances customer loyalty and drives repeat visits, as customers feel more valued and engaged.
5. Efficient Maintenance of Store Equipment
Use Case: With IoT-enabled digital twins, retailers can track the performance of critical store equipment, such as refrigerators, HVAC systems, and lighting. Digital twins can predict when equipment might need maintenance, reducing the risk of unexpected breakdowns.
Benefit: Proactive maintenance extends the lifespan of assets, reduces downtime, and avoids costly repairs. This also ensures a comfortable and functional shopping environment for customers.
6. Product Lifecycle Management
Use Case: Digital twins of products allow retailers to track the entire lifecycle of a product, from manufacturing to end-user usage. Retailers can monitor product performance, returns, and customer feedback to identify trends and improve future product iterations.
Benefit: By better understanding product lifecycles, retailers can enhance product quality, reduce return rates, and ensure customer satisfaction with higher-quality offerings.
7. Streamlining E-commerce Operations
Use Case: Digital twins can model the e-commerce experience, allowing retailers to simulate the online shopping journey, test website changes, and optimize checkout processes. By modeling peak traffic scenarios, retailers can ensure a smooth experience even during high-traffic periods.
Benefit: A seamless e-commerce experience leads to lower cart abandonment rates and higher conversion rates, directly impacting revenue.
8. Visual Merchandising Optimization
Use Case: Digital twins allow retailers to test and visualize merchandising strategies in a virtual environment. They can simulate how different displays and layouts will look and perform before implementing them in the store.
Benefit: Retailers can maximize the impact of visual merchandising, increasing customer engagement with displays, boosting sales, and avoiding costly trial-and-error approaches.
9. Sustainability and Energy Management
Use Case: With a digital twin, retailers can monitor and optimize energy usage in stores. Sensors track energy consumption in real-time, allowing for smart lighting, HVAC adjustments, and more sustainable operations.
Benefit: Reduced energy consumption lowers operating costs and supports sustainability goals, which are increasingly important to consumers and regulatory bodies.
10. Customer Journey Mapping and Analysis
Use Case: Digital twins can map out every step of the customer journey, from entrance to checkout, using data from in-store cameras and IoT sensors. This helps retailers identify high-traffic areas, dwell times, and customer interaction points.
Benefit: By understanding the customer journey, retailers can improve layout, optimize staffing, and reduce pain points, creating a more enjoyable and efficient shopping experience.
Conclusion
Digital twins in retail represent a dynamic shift toward data-driven, customer-focused operations. From enhancing the customer experience to optimizing supply chains, this technology provides a virtual testing ground for ideas and innovations, reducing costs and risks. As the retail landscape becomes increasingly competitive, adopting digital twins can help retailers stay agile and relevant, adapting to evolving customer needs while boosting operational efficiency and sustainability.



